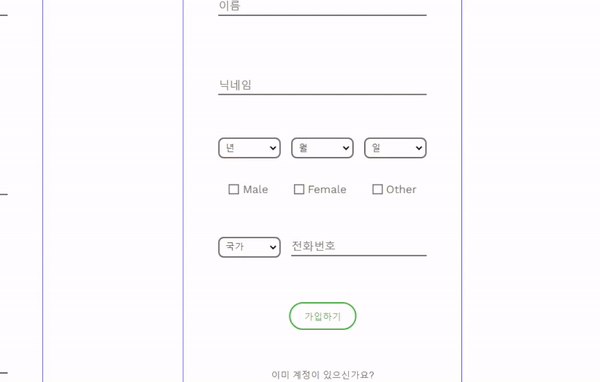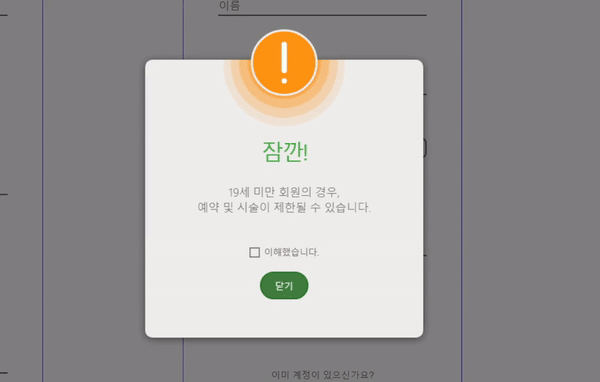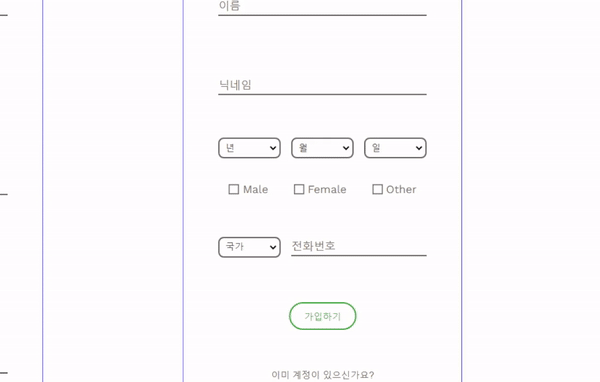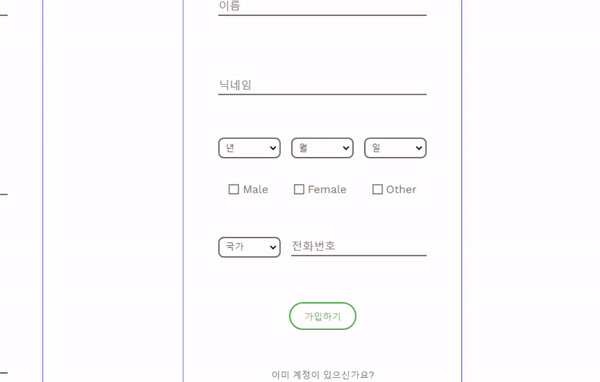
가입 페이지에서 19세 미만의 생년월일을 입력한 경우, 경고 메세지를 담은 모달을 띄우려 한다.
무선 모달창의 구성과 애니메이션을 구현하고, 체크박스를 선택해야만 모달을 닫을 수 있도록 만들었다.
아래는 그 결과물이다.
나이에 따라 팝업 되는 기능을 추가하기에 앞서,
모달 컴포넌트를 재사용할 것을 대비해 모달 내 요소들을 props로 바꾸고, 다른 컴포넌트에 적용하는 실험을 해보았다.
import { useState, useEffect, ReactNode } from "react";
import ReactDOM from "react-dom";
import s from "../stores/styling";
interface ModalProps {
isOpen: boolean;
onClose: () => void;
modalTitle: string;
children: ReactNode;
showCheckbox?: boolean;
checkboxText?: string;
}
const Modal: React.FC<ModalProps> = ({ isOpen, onClose, modalTitle, children, showCheckbox, checkboxText }) => {
const [understand, setUnderstand] = useState(false);
//체크박스 체크 여부 저장
const [animationClosing, setAnimationClosing] = useState(false);
//닫히는 애니메이션울 클래스 추가하는 방식으로 조건부 렌더링
if (!isOpen) return null;
const handleUnderstandChange = (event: React.ChangeEvent<HTMLInputElement>) => {
setUnderstand((prevUnderstand) => !prevUnderstand); //보통 prev라고 쓰지만, 알아보기 쉽게 바꾸어 썼다.
};
const handleModalClose = () => {
if (!showCheckbox || understand) { // 체크박스가 없는 포맷이거나 understand에 체크가 돼있을 때
setAnimationClosing(true) // 모달 닫음으로 처리
setTimeout(() => {
setAnimationClosing(false);
onClose();
}, 800) //애니메이션 duration과 같게 쓴다.
}
};
const portalElement = document.getElementById("portal");
if (!portalElement) return null;
return ReactDOM.createPortal(
<>
<s.Modal className={`modal-overlay ${animationClosing ? "closing" : ""}`}>
<s.Modal className={`modal-wrapper ${animationClosing ? "closing" : ""}`}>
<s.Modal className="circle">
<s.WarnIcon />
</s.Modal>
<s.Echo className="wrapper">
<s.Echo className="circle00" />
<s.Echo className="circle01" />
<s.Echo className="circle02" />
<s.Echo className="circle03" />
</s.Echo>
<s.Modal className="modal-container">
<s.StyledH1 className="warning">{modalTitle}</s.StyledH1>
<s.Modal className="text-box">{children}</s.Modal>
{showCheckbox && <s.Modal className="checkbox-container">
<s.Input
type="checkbox"
id="understand"
checked={understand}
onChange={handleUnderstandChange}
className="modal-check"
/>
<s.Label
htmlFor="understand"
className="understand"
>
{understand ? (
<s.CheckboxAfterIcon className="checkbox-icon-checked" />
) : (
<s.CheckboxBeforeIcon className="checkbox-icon" />
)}
{checkboxText}
</s.Label>
</s.Modal>}
<s.Button className="Round" onClick={handleModalClose}>
닫기
</s.Button>
</s.Modal>
</s.Modal>
</s.Modal>
</>,
portalElement
);
};
export default Modal;
재사용 테스트를 거쳐보니,
props는 손쉽게 사용할 수 있지만 매번 이벤트 핸들러와 state를 다시 써줘야하는 번거로움이 있었다.
이 점을 해결하기 위해 Custom Hook을 사용하여 캡슐화하고, 코드 중복을 더 줄여보자.
사족: 기존 파일과 빈 파일 두개를 나란히 두고 한줄 한줄 이식하듯이(?) 작성하니 보다 이해하기 쉬웠다.
우선 커스텀 훅의 뼈대를 잡는다.
커스텀 훅은 use... 로 시작하며, return 문에 해당 훅이 생성한 값이나 함수를 넣는다.
const useModal = () => {
};
return {
};
export default useModal;
기존 코드에서 useState문과 관련된 부분을 모두 가져오고,
return문에 재사용할 state와 함수를 객체 형태로 반환한다. (배열도 가능하다)
import { useState } from "react";
const useModal = () => {
const [understand, setUnderstand] = useState(false);
const [animationClosing, setAnimationClosing] = useState(false);
const handleUnderstandChange = (
event: React.ChangeEvent<HTMLInputElement>
) => {
setUnderstand((prevUnderstand) => !prevUnderstand);
};
const handleModalClose = () => {
if (understand) {
setAnimationClosing(true);
setTimeout(() => {
setAnimationClosing(false);
onClose(); // Ensure the onClose callback is called when the modal is closed
}, 800);
}
};
return {
understand,
animationClosing,
handleUnderstandChange,
handleModalClose,
};
};
export default useModal;
그리고 인자를 넘겨준다.
나는 여기서 많이 헤멨는데, 아무래도 인수의 개념이 탄탄히 잡히지 않아 그랬던 것으로 보인다.
간단히 말하자면-
1. 커스텀 훅에서 처리할 상태와 함수를 정리해서 보내주면
2. Modal 컴포넌트에서 이것을 인수 (여기서는 모달 열림, 닫힘) 에 따라 처리한다.
import { useState } from "react";
import { UseModalProps } from "../types/ModalProps";
interface UseModalProps { // 인수 타입 선언
isOpen: boolean;
onClose: () => void;
}
const useModal = ({ isOpen, onClose }: UseModalProps) => {
const [understand, setUnderstand] = useState(false);
const [animationClosing, setAnimationClosing] = useState(false);
const handleUnderstandChange = (
event: React.ChangeEvent<HTMLInputElement>
) => {
setUnderstand((prevUnderstand) => !prevUnderstand);
};
const handleModalClose = () => {
if (understand) {
setAnimationClosing(true);
setTimeout(() => {
setAnimationClosing(false);
onClose();
}, 800);
}
};
return {
isOpen,
onClose,
understand,
animationClosing,
handleUnderstandChange,
handleModalClose,
};
};
export default useModal;
여기서 바로 컴포넌트로 넘겨주어도 좋지만, 커스텀 훅에서 써둔 타입 선언부를 컴포넌트에서도 다시 작성해야하는 번거로움을 발견했다.
// 수정 전
interface ModalProps {
isOpen: boolean;
onClose: () => void;
children: ReactNode;
modalTitle: string;
showCheckbox?: boolean;
checkboxText?: string;
}
const Modal: React.FC<ModalProps> = ({
isOpen,
onClose,
children,
modalTitle,
showCheckbox,
checkboxText,
}) => {
const {
understand,
animationClosing,
handleUnderstandChange,
handleModalClose,
} = useModal({ isOpen, onClose });
// 후략
따라서 이번 기회에 타입을 별도 파일로 분리해보았다.
서로 겹치는 부분은 extends 를 사용하여 가급적 겹치지 않게 했다.
// ModalProps.ts
import { ReactNode } from "react";
interface CommonProps {
isOpen: boolean;
onClose: () => void;
}
export interface ModalProps extends CommonProps {
children?: ReactNode;
modalTitle?: string;
showCheckbox?: boolean;
checkboxText?: string;
}
export interface UseModalProps extends CommonProps {}
다시 커스텀 훅으로 돌아와 정리해둔 타입을 불러와 선언해준다.
import { useState } from "react";
import { UseModalProps } from "../types/ModalProps";
const useModal = ({ isOpen, onClose }: UseModalProps) => {
const [understand, setUnderstand] = useState(false);
const [animationClosing, setAnimationClosing] = useState(false);
const handleUnderstandChange = (
event: React.ChangeEvent<HTMLInputElement>
) => {
setUnderstand((prevUnderstand) => !prevUnderstand);
};
const handleModalClose = () => {
if (understand) {
setAnimationClosing(true);
setTimeout(() => {
setAnimationClosing(false);
onClose();
}, 800);
}
};
return {
isOpen,
onClose,
understand,
animationClosing,
handleUnderstandChange,
handleModalClose,
};
};
export default useModal;
첫단계에서 함께한 Modal 컴포넌트 파일에서도 커스텀 훅으로 넘겨준 모든 state와 함수를 지우고, 타입을 선언해준다.
import ReactDOM from "react-dom";
import s from "../stores/styling";
import useModal from "../hooks/ModalHook";
import { ModalProps } from "../types/ModalProps";
const Modal: React.FC<ModalProps> = ({
isOpen,
onClose,
children,
modalTitle,
showCheckbox,
checkboxText,
}) => {
const {
understand,
animationClosing,
handleUnderstandChange,
handleModalClose,
} = useModal({ isOpen, onClose });
if (!isOpen) return null;
const portalElement = document.getElementById("portal");
if (!portalElement) return null;
return ReactDOM.createPortal(
<>
<s.Modal className={`modal-overlay ${animationClosing ? "closing" : ""}`}>
<s.Modal
className={`modal-wrapper ${animationClosing ? "closing" : ""}`}
>
<s.Modal className="circle">
<s.WarnIcon />
</s.Modal>
<s.Modal className="modal-container">
<s.StyledH1 className="warning">{modalTitle}</s.StyledH1>
<s.Modal className="text-box">{children}</s.Modal>
<s.Modal className="checkbox-container">
<s.Input
type="checkbox"
id="understand"
checked={understand}
onChange={handleUnderstandChange}
className="modal-check"
/>
<s.Label htmlFor="understand" className="understand">
{understand ? (
<s.CheckboxAfterIcon className="checkbox-icon-checked" />
) : (
<s.CheckboxBeforeIcon className="checkbox-icon" />
)}
{checkboxText}
</s.Label>
</s.Modal>
<s.Button className="Round" onClick={handleModalClose}>
닫기
</s.Button>
</s.Modal>
</s.Modal>
</s.Modal>
</>,
portalElement
);
};
export default Modal;
이제 다른 컴포넌트에 삽입해보면 이전과 동일한 기능과 효과를 보여주지만 보다 간결하고 깔끔한 코드가 된다.
컴포넌트를 이식(?) 해주고 실제로 여닫히는 상황을 state에 저장할 수 있도록 처리해주면 완성된다.
//LoginPage.tsx
import Modal from "../components/Modal";
const LoginPage = () => {
const [isModalOpen, setIsModalOpen] = useState(false);
const handleOpenModal = () => {
setIsModalOpen(true);
};
const handleCloseModal = () => {
setIsModalOpen(false);
};
//...중략...
}
return (
<>
{/*...중략...*/}
<Modal
isOpen={isModalOpen}
onClose={handleCloseModal}
modalTitle={"잠깐!"}
showCheckbox={true}
checkboxText={"이해했습니다."}
>
<s.StyledP className="modal">
19세 미만 회원의 경우,
<br />
예약 및 시술이 제한될 수 있습니다.
</s.StyledP>
</Modal>
</>
)
}
export default LoginPage;
'React.ts' 카테고리의 다른 글
| GSAP 활용하여 ScrollEvent 쉽게 구현하기 - 1 (0) | 2024.08.07 |
|---|---|
| React TypeScript - OpenAI DALL.E API로 이미지 생성하기 (0) | 2024.07.17 |
| React TypeScript - Intersection Observer 활용 (0) | 2024.07.04 |
| React TypeScript - 카카오맵 API 호출 : TypeError: Cannot read properties of null (reading 'currentStyle') (0) | 2024.06.12 |
| React TypeScript - 카카오맵 API 호출 : TypeError: window.kakao.maps.LatLng is not a constructor 해결하기 (0) | 2024.06.11 |